Which Best Describes the Tertiary Structure of a Protein
A The number of amino acids determines the tertiary structure of the protein. Several types of side chain interactions stabilize the tertiary structure of proteins including which of the following.

Learn About Tertiary Structure Of Protein Chegg Com
The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain backbone with one or more protein secondary structures the protein domains.

. Group of answer choices. Permanent loss of protein structure. Which of the following statements best describes the tertiary structure of a protein.
2 hydrated by water on the surface of the protein. Which of the following best describes the nature of protein primary structure. To some extent the tertiary structure is determined by the amino acid sequence of the primary structure.
The primary structure then is determined by the genetic code with each 3 RNA bases corresponding to a particular amino acid. 09 Which of the following descriptions best describes the tertiary structure of proteins. Which of the following best describes the effect of a greater number of cysteine amino acids on the stability of the proteins.
Amino acids linked together in a specific order by peptide bonds. The number of amino acids determines the tertiary structure of the protein. The primary structure of a protein refers to just the sequence of amino acids in a protein all proteins are basically strings of amino acids usually one hundred or more.
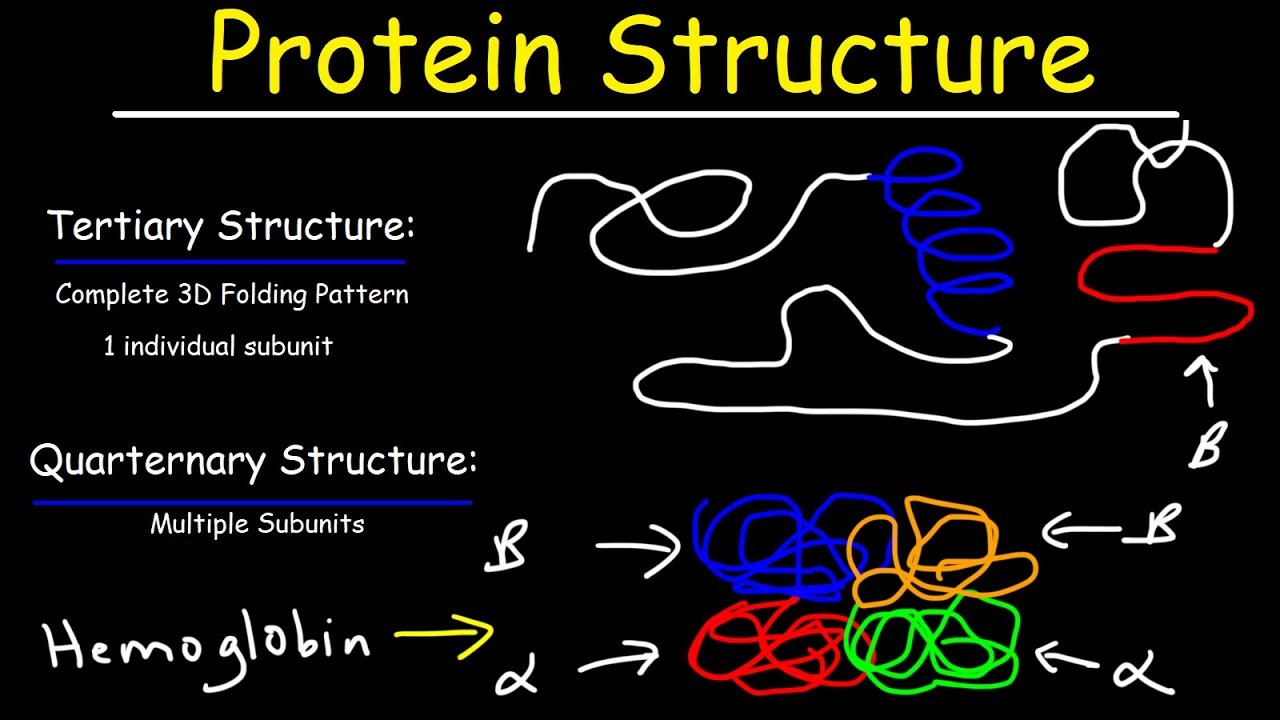
B The interactions of the different RR-groups with other RR-groups and with their environment determine the tertiary structure of the protein. The tertiary structure of a protein is dependent on ligand binding A given protein may have separate binding sites for several different ligands Ligands catalyse biological reactions The binding of the ligand results in the inactivation of the protein. Hemoglobin is a tetramer composed of two different types of globin subunits each of which has an O2 binding site.
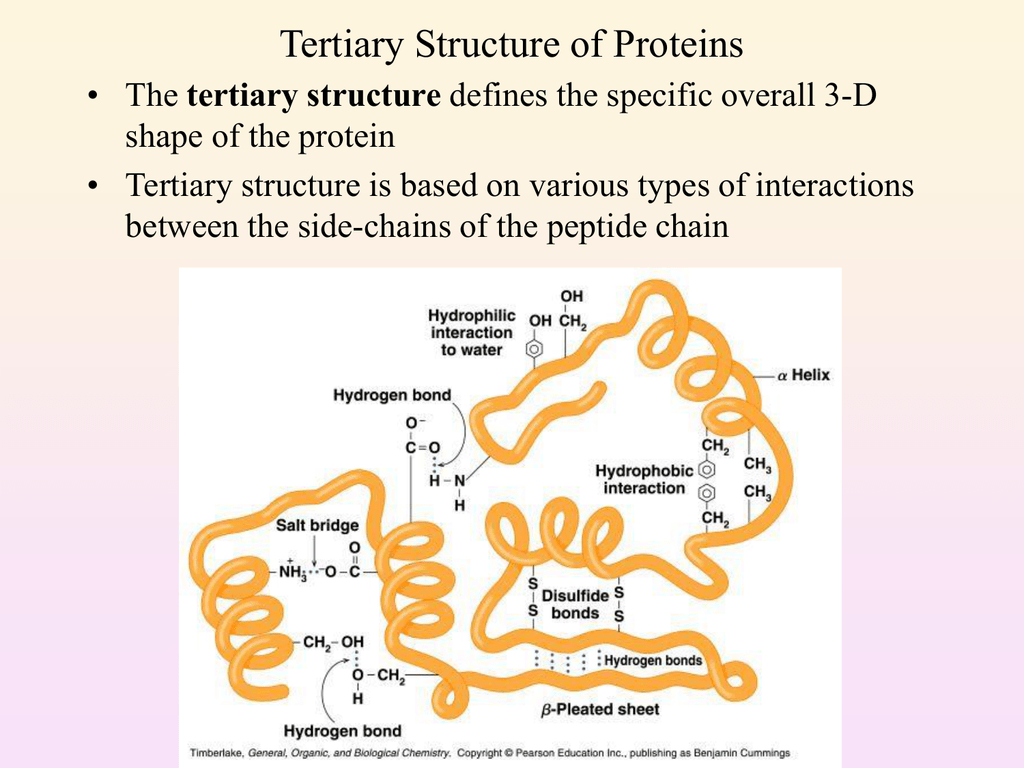
The protein folds so that less of its structure is surrounded by the solvent. The interactions of the different R-groups with other R-groups and with their environment determine the tertiary structure of the protein. The tertiary structure is primarily due to interactions between the R groups of the amino acids that make up the protein.
At the core of this the fact that proteins posses many different hydrophobic or hydrophilic regions. It is generally stabilized by outside polar hydrophilic hydrogen and ionic bond interactions and internal hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar amino acid. Which of the following best describes the location of non-polar amino acid side chains in the tertiary structure of a protein.
After the amino acids form bonds secondary structure and shapes like helices and sheets the structure can coil or fold at random. The linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. Which of the following best describes a feature of proteinligand interactions.
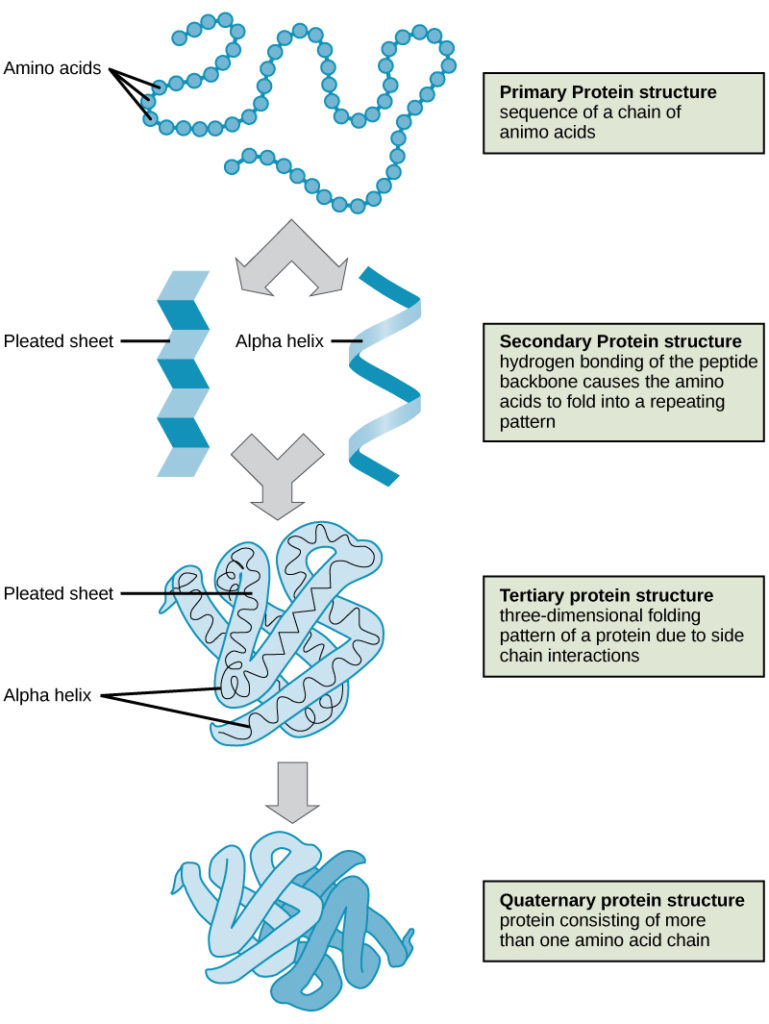
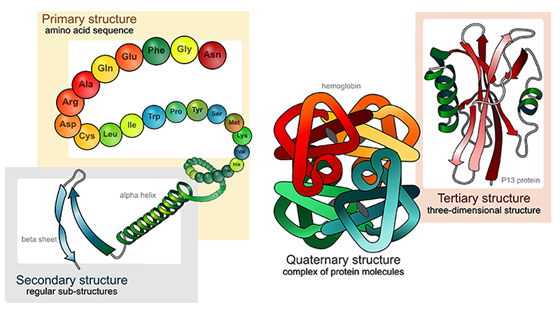
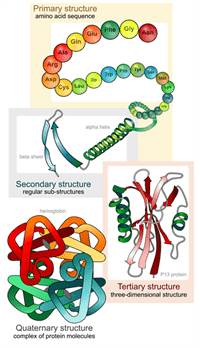
The overall three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide is called its tertiary structure. Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. Primary structure refers to the order of the amino acids in a protein.
The secondary structure is a helix or pleated sheet mad eof hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups. The tertiary structure consists of eight beta-strands connected by α-helices known as the globin fold B. Tertiary structure of a protein describes A The order of amino acids B Location of disulphide bonds C Loop regions of proteins D The ways of protein folding.
1 surrounded by structured water on the surface of the protein. This is what we call the tertiary structure of proteins. For instance in globular proteins the polypeptide chains are held together in a definite way forming a compact structure.
3 concentrated in the interior core of the protein. Proteins fold into their most stable structures. How many types of amino acids.
Hemoglobin is a globular protein composed of a single polypeptide chain that has one O2 binding site. Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. Secondary structure indicates regions of ordered structure and tertiary structure is.
The tertiary structure of a protein refers to the overall three-dimensional arrangement of its polypeptide chain in space. The tertiary structure is a single polypeptide chain that forms a globular shape bonded by hydrogen ionic disulfide and van der Waals bonds or hydrophobic interactions and the interaction between R-groups. R group interactions that contribute to tertiary structure include hydrogen bonding ionic bonding dipole-dipole interactions and.
Complete set of proteins. Question 3 Which of the following best describes how amino acids affect the tertiary structure of a protein. Also intramolecular Hydrogen bonds are key.
Which of the following statements best describes the tertiary structure of a protein. The tertiary structure is maintained by many. The total 3-D conformation of an entire polypeptide chain including a-helices b-sheets and any other loops or bends.
Which of the following best describes how amino acids affect the tertiary structure of a protein. Ionic bonds hydrophobic interactions hydrogen bonds disulfide bonds. The change leads to increased protein stability because of an increased number of S-S bonds in the tertiary structure of the proteins.
The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary. This is the structure that gives protein the 3-D shape and formation. The hydrophobic regions get in the middle away from the solvent.
Specific biological activities such as enzyme activity are associated with the tertiary structure.

Levels Of Protein Organization
Protein Structure Biology For Non Majors I

Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Youtube

Mla Ce Course Manual Molecular Biology Information Resources Genetics Review 3 D Protein Structures

Protein Structure A Level Notes
Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Biology Youtube
Tertiary Structure Of Proteins

Free Protein Structure Biochemistry Homework Page Science Teaching Resources Biology Lessons Teaching Biology
How Is The Tertiary Structure Of Protein Formed Quora

David Chalk Teacherchalky1 Twitter Middle School Science Activities Teaching Biology Medical Student Study

A Primer For Protein Structure Walk In The Forest

Tertiary Structure Protein Structure Tutorials Msoe Center For Biomolecular Modeling
Four Types Of Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Structures

Tertiary Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Primary Secondary Tertiary And Quaternary Structures Of Proteins Youtube

Levels Of Protein Organization

The Thermodynamics Of Protein Folding Depicted As A Free Energy Funnel Biology Forums Gallery Protein Folding Free Energy Thermodynamics

Comments
Post a Comment